fast print
Published:
overview
This solution provides a method for compressing embedded C/C++ debug information. Encode the debug information and generate the coded record, store the coded number in the generated code, output the debug coded number and debug parameters to the PC host software at runtime, the host software finds the format string according to the coded record, and according to the format string formats debug parameters, generate debug information and output.
Current solutions
In the embedded field, debug information is often needed to be added to C/C++ code in order to locate errors and causes or obtain relevant information. At present, the commonly used method is to format the format string through printf or similar functions, generate debug information, and then output it through the serial port or other peripherals.
Disadvantages of current solutions
- A long format string must be saved in the program, which will consume a certain amount of memory space for a microcontroller with limited resources. For example, a simple printf(“Errno %d\n”, 3) takes 10 words for the format string.
- The generated debug information is long. Take the previous printf(“Errno %d\n”, 3) as an example, the generated debug information “Errno 3\n” occupies at least 9 bytes. If the debug information needs to be saved inside the device , it also requires more resources.
- At present, uart is commonly used as a peripheral for outputting debug information. It’s speed is low. Longer debug information will take more time to output. When the debug print is frequently called, it is easy to cause blocking.
Problem to be solved
The technical problem to be solved by this solution is that more memory is occupied due to the long debug information, and the problems that the generated debug information is long and the transmission time of the debug information is long.
Description
Implement the ‘STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU’ macro
#include "macro_paras_opt.h"
#include "macro_struct.h"
#include "macro_type.h"
#define SET_COUNTER(cnt) \ //
FILE_ADDR + cnt;
#ifdef __PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE
#define PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE
#endif
#define GEN_NAME(name) MACRO_CAT(name, __LINE__)
#define _STATIC_PARAS(num, para) PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE para;
#define STATIC_PARAS(num, para) MACRO_PARAS_NOTDEAL_0PARAS(_STATIC_PARAS, para) //
#define STR_PARAS(num, para) MACRO_STR_NUM(para), //
#define STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU(str, ...) \
do \
{ \
MACRO_PARAS_ENUM_OPT(STATIC_PARAS, GEN_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__)); \
GEN_STRUCT_AUTO(GET_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__)); \
SET_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__); \
SET_STRUCT_AUTO(GET_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__)); \
GEN_STRUCT(frame, unsigned char preamble; unsigned char len; unsigned short global_cnt; \
GET_STRUCT_AUTO_TYPE() GET_STRUCT_AUTO_VAR(); \
unsigned char tail;); \
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, preamble) = (0xAA & 0xFC) | (0x00); \
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, len) = sizeof(GET_STRUCT_TYPE(frame)) - 2; \
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, tail) = 0x55; \
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE char *GEN_NAME(fast_print_str) = str; \
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE int GEN_NAME(sizeof_stru_member)[] = {GET_MACRO_PARAS_SIZE(__VA_ARGS__)}; \
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE int GEN_NAME(typeof_stru_member)[] = {GET_MACRO_PARAS_TYPE_FIX(__VA_ARGS__)}; \
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE char *GEN_NAME(fast_print_paras_str)[] = { \
MACRO_PARAS_ENUM_OPT(STR_PARAS, GET_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__))}; \
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, global_cnt) = SET_COUNTER(__COUNTER__); \
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, GET_STRUCT_AUTO_VAR()) = GET_STRUCT_AUTO_VAR(); \
console_output_bin((char *)&GET_STRUCT_VAR(frame), sizeof(GET_STRUCT_TYPE(frame))); \
} while (0)
STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU("hello %d %d %d %d %d", 0, 1, 2, 3, 4); // __LINE__ = 37
macro analysis.
MACRO_PARAS_ENUM_OPT(STATIC_PARAS, GEN_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__)); // generate temporary variables
// static typeof(0) temp_37_5;
// static typeof(1) temp_37_4;
// static typeof(2) temp_37_3;
// static typeof(3) temp_37_2;
// static typeof(4) temp_37_1;
// ;
GEN_STRUCT_AUTO(GET_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__)); // generate temporary structures and variables to store temporary variables
// struct gen_auto37_stru
// {
// typeof(temp_37_5) temp_37_5;
// typeof(temp_37_4) temp_37_4;
// typeof(temp_37_3) temp_37_3;
// typeof(temp_37_2) temp_37_2;
// typeof(temp_37_1) temp_37_1;
// } __attribute__((__packed__)) gen_auto37;
SET_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__); // Initialize temporary variables
// temp_37_5 = 0;
// temp_37_4 = 1;
// temp_37_3 = 2;
// temp_37_2 = 3;
// temp_37_1 = 4;
SET_STRUCT_AUTO(GET_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__)); // Initialize struct variable
// gen_auto37.temp_37_5 = temp_37_5;
// gen_auto37.temp_37_4 = temp_37_4;
// gen_auto37.temp_37_3 = temp_37_3;
// gen_auto37.temp_37_2 = temp_37_2;
// gen_auto37.temp_37_1 = temp_37_1;
GEN_STRUCT(frame, unsigned char preamble; unsigned char len; unsigned short global_cnt; //
GET_STRUCT_AUTO_TYPE() GET_STRUCT_AUTO_VAR(); //
unsigned char tail;); // Generate temporary struct and variable for sending debug info frames
// struct gen_frame37_stru
// {
// unsigned char preamble;
// unsigned char len;
// unsigned short global_cnt;
// struct gen_auto37_stru gen_auto37;
// unsigned char tail;
// } __attribute__((__packed__)) gen_frame37;
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, preamble) = (0xAA & 0xFC) | (0x00); // gen_frame37.preamble = (0xAA & 0xFC) | (0x00);
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, len) = sizeof(GET_STRUCT_TYPE(frame)) - 2; // gen_frame37.len = sizeof(struct gen_frame37_stru) - 2;
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, tail) = 0x55; // gen_frame37.tail = 0x55;
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE char *GEN_NAME(fast_print_str) = str; // Get format string
// PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE char *fast_print_str37 = "hello %d %d %d %d %d";
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE int GEN_NAME(sizeof_stru_member)[] = {GET_MACRO_PARAS_SIZE(__VA_ARGS__)}; // Get debug parameter bit width
// PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE int sizeof_stru_member37[] = {(sizeof(0)), (sizeof(1)), (sizeof(2)), (sizeof(3)), (sizeof(4)), (0), (0), (0), (0), (0)};
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE int GEN_NAME(typeof_stru_member)[] = {GET_MACRO_PARAS_TYPE_FIX(__VA_ARGS__)}; // Get debug parameter type
// PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE int typeof_stru_member37[] = {(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), char) ? 1 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), unsigned char) ? 2 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), short) ? 3 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), unsigned short) ? 4 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), int) ? 5 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), unsigned int) ? 6 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), float) ? 7 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), double) ? 8 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))),
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), char) ? 1 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), unsigned char) ? 2 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), short) ? 3 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), unsigned short) ? 4 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), int) ? 5 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), unsigned int) ? 6 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), float) ? 7 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), double) ? 8 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))),
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), char) ? 1 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), unsigned char) ? 2 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), short) ? 3 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), unsigned short) ? 4 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), int) ? 5 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), unsigned int) ? 6 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), float) ? 7 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), double) ? 8 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))),
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), char) ? 1 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), unsigned char) ? 2 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), short) ? 3 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), unsigned short) ? 4 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), int) ? 5 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), unsigned int) ? 6 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), float) ? 7 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), double) ? 8 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))),
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), char) ? 1 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), unsigned char) ? 2 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), short) ? 3 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), unsigned short) ? 4 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), int) ? 5 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), unsigned int) ? 6 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), float) ? 7 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), double) ? 8 :
// (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))), 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE char *GEN_NAME(fast_print_paras_str)[] = { //
MACRO_PARAS_ENUM_OPT(STR_PARAS, GET_TEMP_VARS(__VA_ARGS__))}; // PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE char *fast_print_paras_str37[] = {
// "temp_37_5",
// "temp_37_4",
// "temp_37_3",
// "temp_37_2",
// "temp_37_1",
// };
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, global_cnt) = SET_COUNTER(__COUNTER__); // gen_frame37.global_cnt = 0 + 1; ;
GET_STRUCT_VAR_MEMBER(frame, GET_STRUCT_AUTO_VAR()) = GET_STRUCT_AUTO_VAR(); // gen_frame37.gen_auto37 = gen_auto37;
console_output_bin((char *)&GET_STRUCT_VAR(frame), sizeof(GET_STRUCT_TYPE(frame))); // console_output_bin((char *)&gen_frame37, sizeof(struct gen_frame37_stru));
result.
do
{
static typeof(0) temp_37_5;
static typeof(1) temp_37_4;
static typeof(2) temp_37_3;
static typeof(3) temp_37_2;
static typeof(4) temp_37_1;
;
struct gen_auto37_stru
{
typeof(temp_37_5) temp_37_5;
typeof(temp_37_4) temp_37_4;
typeof(temp_37_3) temp_37_3;
typeof(temp_37_2) temp_37_2;
typeof(temp_37_1) temp_37_1;
} __attribute__((__packed__)) gen_auto37;
temp_37_5 = 0;
temp_37_4 = 1;
temp_37_3 = 2;
temp_37_2 = 3;
temp_37_1 = 4;
gen_auto37.temp_37_5 = temp_37_5;
gen_auto37.temp_37_4 = temp_37_4;
gen_auto37.temp_37_3 = temp_37_3;
gen_auto37.temp_37_2 = temp_37_2;
gen_auto37.temp_37_1 = temp_37_1;
struct gen_frame37_stru
{
unsigned char preamble;
unsigned char len;
unsigned short global_cnt;
struct gen_auto37_stru gen_auto37;
unsigned char tail;
} __attribute__((__packed__)) gen_frame37;
gen_frame37.preamble = (0xAA & 0xFC) | (0x00);
gen_frame37.len = sizeof(struct gen_frame37_stru) - 2;
gen_frame37.tail = 0x55;
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE char *fast_print_str37 = "hello %d %d %d %d %d";
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE int sizeof_stru_member37[] = {(sizeof(0)), (sizeof(1)), (sizeof(2)), (sizeof(3)), (sizeof(4)), (0), (0), (0), (0), (0)};
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE int typeof_stru_member37[] = {(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), char) ? 1 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), unsigned char) ? 2 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), short) ? 3 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), unsigned short) ? 4 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), int) ? 5 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), unsigned int) ? 6 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), float) ? 7 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), double) ? 8 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(0), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))),
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), char) ? 1 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), unsigned char) ? 2 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), short) ? 3 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), unsigned short) ? 4 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), int) ? 5 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), unsigned int) ? 6 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), float) ? 7 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), double) ? 8 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(1), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))),
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), char) ? 1 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), unsigned char) ? 2 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), short) ? 3 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), unsigned short) ? 4 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), int) ? 5 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), unsigned int) ? 6 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), float) ? 7 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), double) ? 8 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(2), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))),
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), char) ? 1 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), unsigned char) ? 2 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), short) ? 3 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), unsigned short) ? 4 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), int) ? 5 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), unsigned int) ? 6 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), float) ? 7 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), double) ? 8 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(3), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))),
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), char) ? 1 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), unsigned char) ? 2 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), short) ? 3 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), unsigned short) ? 4 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), int) ? 5 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), unsigned int) ? 6 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), float) ? 7 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), double) ? 8 :
(__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(4), typeof(const char *)) ? 9 : 0))))))))), 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE char *fast_print_paras_str37[] = {
"temp_37_5",
"temp_37_4",
"temp_37_3",
"temp_37_2",
"temp_37_1",
};
gen_frame37.global_cnt = 0 + 1;
;
gen_frame37.gen_auto37 = gen_auto37;
console_output_bin((char *)&gen_frame37, sizeof(struct gen_frame37_stru));
} while (0);
- Use the macro STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU instead of printf to achieve debug information generation. In STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU(“Errno %d\n”, 3), “Errno %d\n” is called the format string, and “3” is called the debug parameter.
- Use the compiler predefined macro COUNTER to indicate the number of STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU in the current C file. STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU uses COUNTER to obtain the effective sequence number of the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU in the current C file.
- STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU generates a unique STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address for the entire project according to the starting address of the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address space and the valid sequence number. The STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address (‘SET_COUNTER’) is an integer that encodes debug information. The bit length can be adapted according to the needs of the project. The 2-byte STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address space contains 65536 STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU addresses.
- STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU generates structure types and variables according to the debug parameters. The structure member types correspond to the debug parameter types one-to-one. The structure members are aligned with a single byte, and the values of the structure variable members are initialized to the values of the debug parameters.
- Obtain format string, debug parameter type, debug parameter bit width, STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU calling line number, debug parameter structure class size (in bytes) through STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU.
- Call the debug information output driver through STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU, pass the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address, the pointer of the debug parameter structure variable, and the size of the debug parameter struct to output the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address value and debug parameter value.
- Use a predefined macro PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE to control the expansion result of STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU in the preprocessing phase of project preprocessing and project compilation.
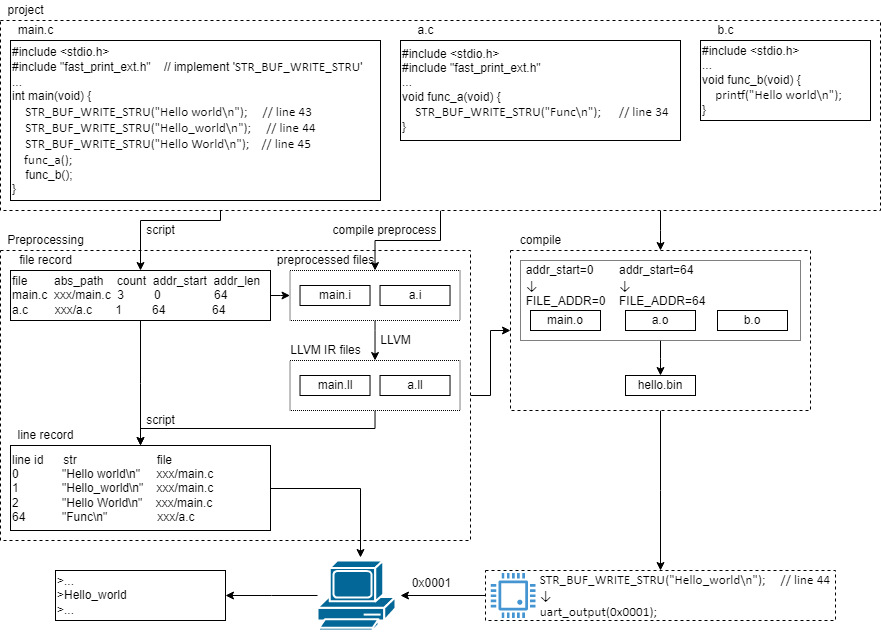
Preprocessing
- Use the script to traverse the entire project, record all C files that directly call STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU, and the number of occurrences of STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU in each file.
- According to the recorded file and the number of occurrences of STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU in the file, allocate a section of STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address space for each file. The length of the address space of the file should not be less than the number of occurrences of STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU in the file, and there is no overlap between any file address spaces. The starting address of the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address space is passed into the file in the form of a predefined macro at compile time, which is represented by FILE_ADDR below.
- The recorded C file is preprocessed with a preprocessor to generate a preprocessed file. When preprocessing each C file, pass the corresponding FILE_ADDR and ‘PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE=static’ to the file as predefined macros. Corresponding to each STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU call place, a global debug parameter structure class and variables are generated, and a global variable containing format string, debug parameter type, debug parameter bit width information, and a global one containing the calling line number, STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address information variables. Use the script to analyze the files generated by the preprocessing, and obtain the line number of the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU call, the address of the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU, and the format string information.
- Use clang to compile preprocessed files to generate LLVM IR files. Use software tools to analyze the LLVM IR file to obtain the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU format string, debug parameter type, and debug parameter bit width information.
- Generate the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU call record file according to the call line obtained by STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU, STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address, format string, debug parameter type, and debug parameter bit width information. The file contains the calling line number of STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU, format string, debug parameter type, debug parameter bit width and the file path with the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address as the index.
Compile
For recorded C files containing STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU, FILE_ADDR and ‘__PYTHON_SCOPE_PRE=’ are passed to each file as predefined macros when compiling. Corresponding to each STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU call place, generate a local variable including the debug parameter structure class and variables, the size of the debug parameter structure class, the address of STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU, and the debug information output driver calling code.
Run
Before the program runs, run the PC host software and the terminal display program on the PC side. The PC host software is used to open the debug interface connected to the PC, and connect the terminal display program through the TCP port. Putty can be used as a terminal display program. The PC host software reads the information in the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU call record file and waits for the input of the debug interface.
When the program runs to the place where STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU is called, the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address value and the debug parameter value are output by the output interface in the form of a byte stream.
After receiving the byte stream, the PC host software analyzes the byte stream, first obtains the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU address, retrieves the STR_BUF_WRITE_STRU call record file, and finds the corresponding record. Then, according to the format string, debug parameter type, and debug parameter bit width information in the record, the debug parameter data is converted into debug information, and output to the terminal display program.
Repository
Git repository:
github.com/novumdun/fast-print
